GNSS Frequency Bands
The GNSS Bands are the range of radio frequencies used by different satellite constellations to broadcast signals from satellites to Earth and vice versa. There are 4 Global Coverage Satellite Constellations and 2 Regional Coverage constellations,
- GPS ( Global )
- GLONASS ( Global )
- Galileo ( Global )
- BeiDou ( Global )
- IRNSS ( Regional )
- QZSS ( Regional )
GNSS Frequencies
| GNSS Constellation | Number of Satellites | Frequency Bands | Orbit Altitude | Country/Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPS (United States) | 31+ (constellation) | L1: 1575.42 MHz L2: 1227.60 MHz L5: 1176.45 MHz L1C: 1575.42 MHz L2C: 1227.60 MHz L5C: 1176.45 MHz | Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) | United States |
| GLONASS (Russia) | 24+ (constellation) | L1: 1598.0625-1605.375 MHz L2: 1242.9375-1248.625 MHz L3: 1202.025-1202.025 MHz | Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) | Russia |
| Galileo (European Union) | 26 (constellation) | E1: 1575.42 MHz E5a: 1176.45 MHz E5b: 1207.14 MHz E5 AltBOC: 1191.795 MHz E6: 1278.75 MHz | Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) | European Union |
| BeiDou (China) | 35+ (constellation) | B1: 1561.098 MHz B2: 1207.14 MHz B3: 1268.52 MHz B1C: 1575.42 MHz B2a: 1176.45 MHz B2b: 1207.14 MHz | Medium Earth Orbit (MEO/IGSO) | China |
| QZSS (Japan) | 4+ (constellation) | L1: 1575.42 MHz L2C: 1227.60 MHz L5: 1176.45 MHz L6: 1278.75 MHz | Quasi-Zenith Orbit (QZO) | Japan |
| NavIC (India) | 7 (constellation) | L5: 1176.45 MHz S: 2492.028 MHz | Geostationary Orbit (GEO) | India |
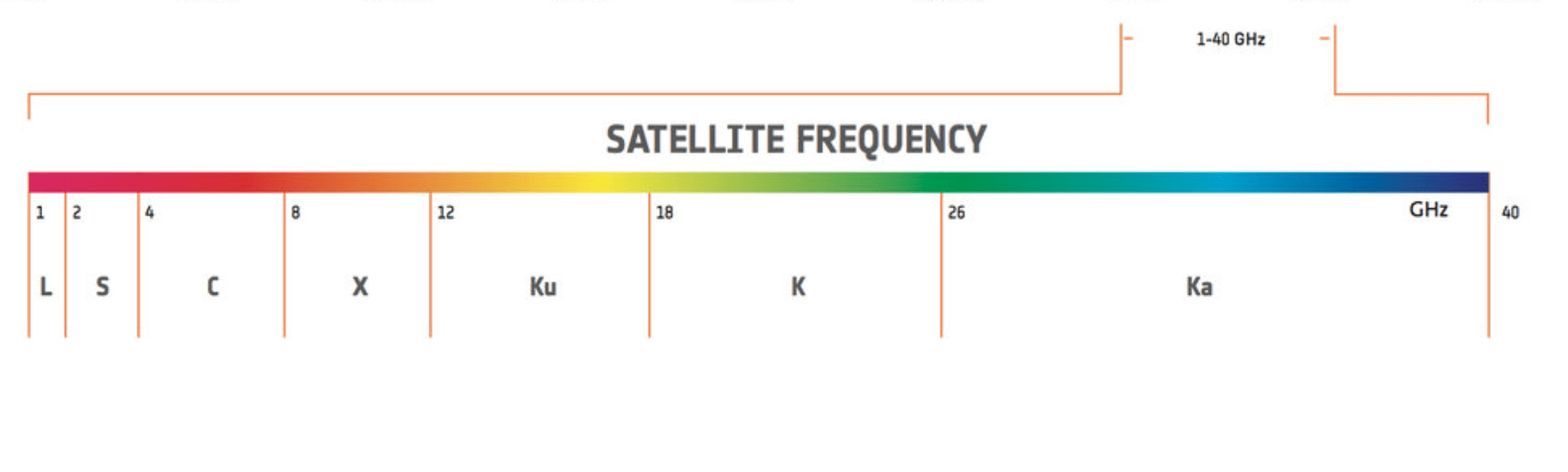
Satellite Frequency bands and their Signal Characteristics
There are 7 satellite frequency bands and that are,
- L-band ( 1–2 GHz )
- S-band ( 2–4 GHz )
- C-band ( 4–8 GHz )
- X-band ( 8–12 GHz )
- Ku-band ( 12–18 GHz )
- K-band ( 18-27 GHz )
- Ka-band ( 27–40 GHz )
L-band ( 1–2 GHz )
This band of frequencies are used in the GPS carriers and for communication using the satellite phones and mostly civilian GNSS services. This range of bands are suitable for these applications because of its ability to penetrate clouds and foliage.
S-band ( 2–4 GHz )
The S-Band frequencies are used for scientific and military applications because of its better accuracy and precision. Most weather radar, ship radar and even the communication of the Space agencies with ISS is in this frequency band.
C-band ( 4–8 GHz )
C-Band is used for Satellite TV, Aviation and marine navigation. This is because of the property of this band which is resilient to signal interference from weather conditions. Most TV networks and satellite feeds use this band mostly in the dense forest area since its much more resilient to rain fade.
X-band ( 8–12 GHz )
Primarily used for military purposes, the application on X-band frequencies are used in continuous-wave radar, SAR radar and other radar systems. Thus, this frequency band is used for applications such as air traffic, aviation, weather monitoring, defense in the military and speed detection by the police.
Ku-band ( 12–18 GHz )
This band is used for satellite communications. This is mostly used for direct broadcast satellite services to transmit broadcast satellite television. This band is mostly susceptible to rain fading.
K-band ( 18-27 GHz )
This Frequency range is the center of the K-Band and is absorbed by the water vapor in the atmosphere. Thus, this is absorbed easily, this cannot be used for any long range communications. This is one of the band that get degraded easily in the atmosphere beyond usefulness.
Ka-band ( 27–40 GHz )
The Ka-Band is used in satellite communication since the communication demands a high frequency and bandwidth for higher data transmission rates. This is used by focusing a single beam or multiple beam of radio frequencies. Thus, this is focused, the same frequency can be reused for higher coverage and data transmission rate. Even the Kepler Space Telescope sent the data it collected in space to the Earth using the Ka-Band.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GNSS uses various frequency bands to provide position and navigation services across the globe. Each satellite constitution uses a specific band of frequencies and each band has its own advantages and disadvantages as mentioned above. Understanding these frequency bands are crucial in utilizing the satellite technology effectively in various domains.