LiDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging whereas LaDAR stands for Laser Detection and Ranging. Generally, Both Ladar and Lidar are called Lidar but the main difference is that a Lidar can have any light source such as, infrared, UV Laser, Visible light and even laser. But when it comes to LaDAR, Laser will be used as the Source. To put it simply, LiDAR is a generalized term where any light source can be used whereas LaDAR is specific where only Laser is used as source.
LiDAR LaDAR Comparison:
| LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) | LaDAR (Laser Detection and Ranging) | |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Light Detection and Ranging | Laser Detection and Ranging |
| Technology | Uses light pulses (typically infrared) to measure distances to objects. | Uses laser pulses (visible or invisible) to measure distances to objects. |
| Principle | Measures time taken by light to bounce back from objects to calculate distances. | Measures time taken by laser pulses to bounce back from objects to calculate distances. |
| Application | Widely used in autonomous vehicles, mapping, forestry, archaeology, etc. | Commonly used in industrial settings, atmospheric research, object detection, etc. |
| Range | Generally shorter range compared to LaDAR. | Typically longer range compared to LiDAR. |
| Cost | Often less expensive than LaDAR systems. | Generally more expensive than LiDAR systems. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy for short-range measurements. | High accuracy for long-range measurements. |
| Usage | Popular for terrestrial mapping and point cloud generation. | Used in aerial mapping and topographic surveys. |
| Limitations | Sensitive to weather conditions (rain, fog) affecting performance. | Susceptible to interference from certain materials and atmospheric conditions. |
| Advantages | Lower cost, compact size, and good for short-range applications. | Longer range capabilities and excellent performance in long-distance measurements. |
LaDAR – Laser Detection And Ranging
LaDAR, also known as the Laser Radar, is a laser-based remote sensing technique similar to LiDAR. This is called Laser Radar figuratively but this has to be in no way confused with Radar. However, Lidar and Ladar are similar, the main difference is that Lidar focuses on measuring the distance between the source and object and creating 3d maps with it. Whereas, LaDAR focuses primarily on detecting and identifying objects in its Field Of View.
How LaDAR works
LaDAR systems pulses lasers towards a target and the reflected light is analyzed to identify the object. The LaDAR system typically measures the intensity and the wavelength of the reflected laser light which can aid in target detection.
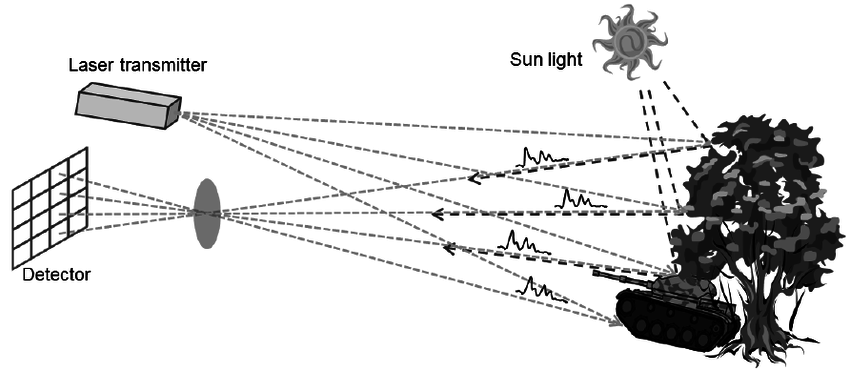
Applications of LaDAR
Military and Defense: LaDAR is extremely useful for military surveillance and also in target tracking and intelligence gathering.
Aerospace: LaDAR’s primary purpose of target detection makes it really useful in obstacle detection, terrain mapping and collision avoidance in aircrafts and spacecrafts.
Target Tracking: Ladar’s precise object detection capabilities makes it valuable in various applications such as in the security systems and object identifications.
Remote Sensing: The object detection and mapping capability of the Ladar system makes it a go to option for remote sensing applications where object detection is the main priority.
LiDAR – Light Detection And Ranging
LIDAR stands for Light Detection and Ranging. It is used in generating 2d and 3d maps of the environment primarily by using two measurement techniques, TOF ( Time Of Flight } and Triangulation. Though lidar can be used for many applications, its primary use case is in autonomous vehicles for generating a 2d or 3d map of their environment and using the generated map to Localise ( Finding where the vehicle is by comparing with the generated map ) and navigate to the destined location.
How LiDAR works:
A Light source such as InfraRed Source is mounted on top of a rotating plate and the light source sends out a beam of light at a particular frequency and waits for the light to reflect off of a surface. By calculating the time taken for the light to be received, the distance between the source and the object is determined. Since the Light source is placed on top of a rotating platform, the platform can be rotated to every angle and the object at 360° is captured and a 2D map is generated. When multiple light sources are stacked on top of each other and the same process is repeated, we get a 3D mapping of the environment.

Applications of LiDAR
Robotics: The main place where lidar is used is in the Autonomous vehicles and Autonomous robots. The use of lidar here is for localisation and navigation purposes.
Aerial Inspection: The lidar is mounted on top of a Drone or a UAV and it is used for industrial inspections, powerline inspections, industrial asset monitoring and so on.
Agriculture: Lidar along with other sensors is used in Agriculture for identifying location to irrigate instead of irrigating the entire area thus saving water and other resources.
Lidar in Space: Lidar is used in robots that are mapping the other planets and natural satellites like the moon. But one other peculiar use case that I first hand saw for the use of lidar in space is for docking in space.
Conclusion
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) and Ladar (Laser Detection and Ranging) are both remote sensing techniques that use light pulses to measure object’s distances. The main difference is the light source: lidar uses any light source and whereas the ladar uses laser as the light source. LiDAR is commonly used in terrestrial mapping and autonomous vehicles, while LaDAR is primarily used for military surveillance, aerospace, target tracking and object detection.



Pingback: LiDAR vs Radar vs Sonar : Working, Difference and Comparisons. - LIDAR and RADAR