Global Satellite Navigation System or Global Navigation Satellite System ( GNSS ) is the constellation of satellites that orbits earth positioned in Medium Earth Orbit ( MEO ) which provides position information to the receivers on the ground.
The Global Satellite Navigation System has revolutionized the modern way of navigating and finding position on the Earth. The application of satellite navigation was intended for the military at first but it spread wide into applications such as robotics, fitness tracking and more. This is achieved with the help of the network of satellites providing global coverage, allowing its users to navigate and find their location.
The Evolution of Navigation Technology
In the past, humans relied on various different methods to navigate such as looking at the stars, compasses, landmarks and so on. However, these methods are not so reliable, less accurate and cannot be used based on weather conditions and long distance journeys.
The birth of the Global Satellite Navigation System made a significant advancement in the navigation technology. The concept of satellite navigation originated with the United State’s ‘Global Positioning System’ ( GPS ) launched in the year 1970. Though it was developed for military purposes, it was later made available for civilian uses.
The successful implementation of the United States GPS made other countries implement their own Global Satellite Navigation System which are,
- Globalnaya Navigazionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema as GLONASS ( Russia ),
- Galileo ( Europe ),
- BeiDou Navigation Satellite System as BDS ( china ),
- Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System as IRNSS / Navigation Indian Constellation as NavIC ( India ),
- QZSS ( Japan )
How GNSS Work
Global Navigation Satellite System operates through a network of satellites orbiting the Earth at a precise orbit and at precise positions and speed. The GNSS is not just the satellites in space. The Global Satellite Navigation System consists of 3 segments,
- Space Segment
- Control Segment
- User Segment
Space Segment
The space segment in the GNSS is one of the most important and critical components. This consists of the networks of satellites deployed in the Medium Earth Orbit ( MEO ), where it is ensured that the satellites are covering the globe at most times. Thus, more than one satellite is launched as a part of each GNSS program for fault tolerance and improved accuracy.
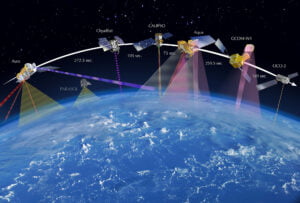
Satellite Constellation
The GNSS satellites follow constellations that are positioned in a way that ensures that there are at least four satellites visible from any point on the earth. The GNSS satellites are MEO ( Medium Earth Orbit ) satellites and are placed at around 20,180 km (12,540 mi) from the Earth.
Satellite Characteristics
The satellites in GNSS constellations are equipped with precise atomic clocks to maintain accurate time keeping. This is because the position is calculated with the help of the distance from the satellite to the receiver on earth. This is done by calculating the round trip time for the signal to travel from satellite to receiver. Thus, a precise clock is needed and atomic clocks are used. The satellites broadcast these clock time and its position data thus can be used in triangulating the position. The data needs to be a transmitter so, radio transmitters are also equipped to the satellites.
Control Segment
The control segment oversees the operation of satellites and ensures integrity and accuracy of the transmitted GNSS signals. This consists of ground control stations and monitoring facilities that monitors and does error correction.
These Ground Stations are responsible for the tracking of the satellite orbit and monitoring of the health and sending orbital corrections and adjustments. These stations maintain constant communication with the satellites and compare with the known current position of the stations and create an error value which can be used in differential GPS for better accuracy.
These Ground stations are also responsible for the Time Synchronization in the GNSS satellites. These stations correct the satellites clocks and synchronize them with the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC ) providing the satellites with reliable time references.

User Segment
The User Segment in the GNSS is the end-user. The individuals, the businesses and industries that use the data from the GNSS satellites are the User Segment. This contains the GNSS receivers that are capable of decoding the signal from the satellites and calculate the users position, velocity and time.
When receivers receives the signal from multiple satellites, it uses signal processing algorithm to extract the timing information. Then the data is compared with the arrival time and the difference is used to find the distance between the satellites and using this, triangulation is performed to find the accurate position.

Applications of GNSS:
- Navigation in transportation modes.
- Precision agriculture for optimized farming practices .
- Disaster management and search & rescue operations.
- Location-Based Services (LBS) in smartphones.
- Surveying and mapping for accurate geospatial data.
For More Applicaitions of GNSS, Read – Applications of GPS
Limitations of GNSS:
- Signal obstruction in urban areas and dense building areas.
- Multipath interference from signal reflections.
- Atmospheric effects affecting signal accuracy.
- Vulnerability to signal jamming and spoofing.
- Reliance on satellite constellation for system functionality.
Conclusion
Finally, the Global Satellite Navigation System has modernized the navigation in the current world. However, the GNSS is not without any limitations. Despite all its challenges, GNSS remains a crucial technological development that has a significant impact on modern society.