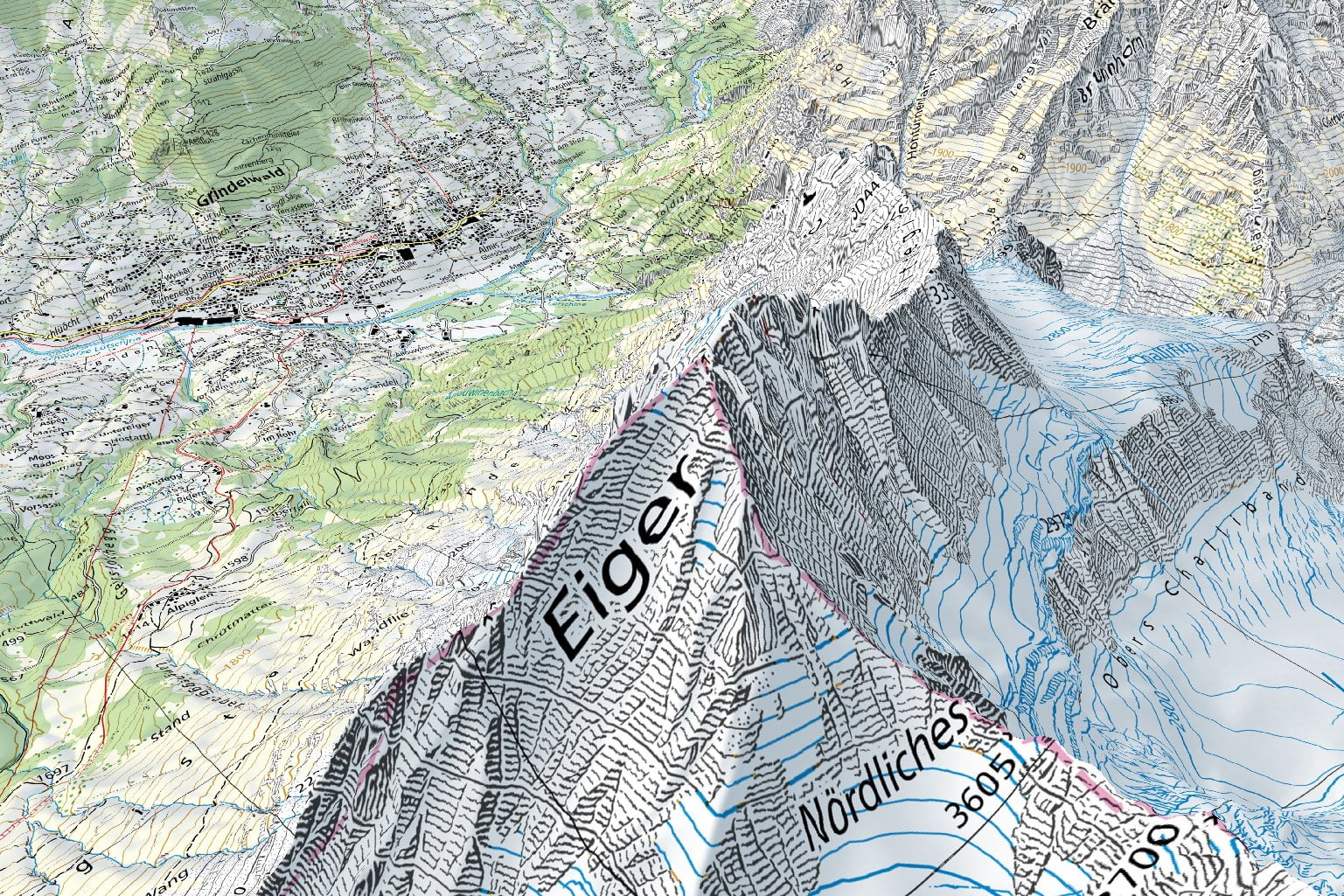
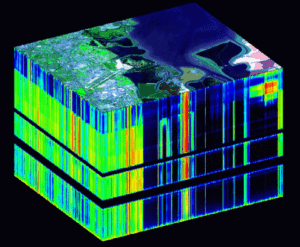
The main action that contributed to the development of today’s modern society is the power of spatial information. From tracking the weather to mapping and planning cities, spatial technologies play an important role. The two key players in this is Remote Sensing and Geographical Information System ( GIS ). The Both serve different purposes but the cooperation between these technologies drives the advancements in data analysis, visualization and informed decision making.
Remote Sensing Vs Geographic Information Systems ( GIS ) Comparison
| Aspect | Remote Sensing | GIS |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collects info about objects from a distance | Manages, analyzes, and visualizes spatial data |
| Data Acquisition | Uses sensors, satellites, drones, etc. | Gathers data from various sources |
| Data Types | Imagery and sensor data | Vector (e.g., roads) and grid (e.g., temp.) data |
| Focus and Application | Capturing real-world data and changes | Analyzing and interpreting data |
| Technology and Tools | Satellites, drones, various sensors | Software platforms (ArcGIS, QGIS) |
| Role | Data collection | Data visualization and analysis |
| Challenges | Data integration, formats, projections | Aligning data for accurate analysis |
What is Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing in a nutshell means, collecting information about objects or a phenomena from a distance. This can be done using various platforms, including satellites, drones, aircrafts and different types of sensors. By capturing electromagnetic radiation, these platforms mentioned above will create an image and data that provides information about the environment. Remote Sensing’s application span in a wide area, from monitoring land covers to monitoring deforestation to tracking weather patterns and mapping natural disasters. Remote Sensing on the whole is a non-intrusive way in understanding the Earth’s dynamics.

What is Geographic Information Systems ( GIS )
On the other hand, GIS is designed to manage, analyze and visualize spatial data. A GIS combines different types of data: both spatial and non spatial into a unified system, providing a single view of geographic information. GIS allows users to query and analyze the data, generate maps and model scenarios. This technology finds application in city planning, natural resource management, logistics and furthermore. By layering different types of data, above another, GIS is used in understanding the relationship between one phenomena and another which might be otherwise hard to find.

Differences Between Remote Sensing and GIS
While both the Remote Sensing and GIS deals with the Earth’s data, they both have different roles and approaches.
1. Data Acquisition
Remote Sensing employs different types of active and passive Sensors to capture the data from a distance without interfering with the environment. Passive sensors detect natural radiations emitted or reflected by objects, whereas the active sensors emit their own radiation to interact with the object and collect data based on the interaction of the object.
Whereas GIS, focuses more on managing and analyzing existing spatial and non spatial data, which comes from various sources and providing useful insights.
2. Data Types
Remote sensing primarily deals with imagery and sensor data. Satellite images and aerial photographs are used in finding insights about the Earth’s surface, used in finding changes over time.
In GIS, data is categorized into vectors and grid formats. Vector data represents objects with high precision (e.g., roads, buildings), while gridded data uses a grid of cells to represent continuous phenomena (e.g., temperature, precipitation).
3. Focus and Application
Remote sensing focuses on capturing the real world data and their changes. It provides information on the spatial phenomena and their changes.
GIS, on the other hand. Is more concerned with analyzing and interpreting the data to come to get a useful insight. It is used in making an informed decision.
4. Technology and Tools
Remote Sensing relies on a wide range of technologies such as satellites, drones and aircraft and wide varieties of sensors such as radars, lidars and cameras to capture data.
GIS employs special software platforms such as ArcGIS and QGIS to process, analyze and visualize spatial data. These tools are used to create interactive maps and perform spatial queries.
Synergy and Collaboration
In a nutshell, Remote Sensing is used in collecting the data from various sources and GIS is used in visualizing and analyzing the collected data for informed decision making.
1. Complementary Roles
Remote Sensing data, such as the high-resolution satellite imagery, serves as a valuable input for GIS. This data can be used to update the existing GIS databases and can be used to monitor changes over time. While GSI gives context and analyzing capability to the raw data collected through remote sensing.
2. Case Studies
Consider the monitoring of deforestation around the globe. Satellite imagery captures the changes in the forest cover over time, while GIS helps in understanding the extent of deforestation, identify areas most affected and model the impact of it.
3. Challenges in Integration
Integrating data from different remote sensing sources into the GIS is a current challenge. Data format, projections and scales must align for accurate analysis. A simple way of expressing coordinates in DMS and DD needs converting the coordinate from Degree, Minute, Second ( DMS ) to Degree Decimal ( DD ) and vice versa. This can require more computing resources if it is converted for every point which can be huge. Combined efforts and advanced tools are needed to overcome this problem.
Conclusion
Remote Sensing and GIS are two completely different fields. Where Remote Sensing focuses more on collecting more detailed and accurate data and logging them without interfering much into the ecosystem. Whereas GIS is more like a way of analyzing the collected data and visualizing them by layering one on top of another to make informed decisions. Both work hand in hand but are completely different in nature.