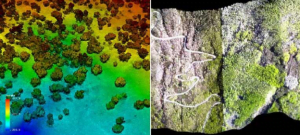
LIDAR is a system that uses a near-infrared beam of laser light to illuminate target objects to calculate the distance between the LIDAR sensor and the objects of interest. Given the constant speed at which light travels through air, the process of distance determination is fast, and the data collected is of incredibly high precision.
Moreover, the flight of laser light pulses and light speed are vital in figuring out the target’s distance from the light source. Because several laser beams of light can be transmitted simultaneously, sweeping a vast surface, large quantities of reliable data can be gathered using LIDAR systems.
Like any other technology piece, LIDAR systems have their strengths and limitations, which this article will attempt to explore.
Pros of LIDAR
- High data precision and 3D image resolution
LIDAR technology used highly sophisticated sensors that can capture object data 2500 meters away. As such, the 3D imaging constructed from cloud points has a relatively high resolution. The high accuracy level achieved in data collection is mostly enhanced by the constant airspeed enabling real-time information gathering and distance calculation.
- The massive quantity of data collected.
The latest technological advancement in LIDAR technology is the 3D LIDAR systems. 3D LIDAR sensors are designed to transmit several laser beams of light over a wider geographical area. For example, in forestry, large footprint 3D LIDAR systems emit laser beams with a larger diameter. The area scanned during data collection is very large. Thus massive 3D data is gathered during this process, which makes LIDAR technology cost-effective from this perspective.
- High speed in data gathering and object distance calculation
Considering the speed of light in the air is incredibly fast and constant, the time of flight of the near-infrared laser light emitted from the LIDAR sensor is in nanoseconds, thus accelerating the process of data collection and object distance determination. That is one of the primary attributes that makes LIDAR technology superior over other data collection systems, such as cameras.
- Larger radial object range
Unlike cameras, LIDAR systems can conveniently scan and detect target objects that are more than 100 meters away. This characteristic makes LIDAR technology a suitable option in forestry management as well as autonomous vehicle driving. Whereas massive information from a wider area can be obtained from using LIDAR technology, the accuracy of data collected over 200 meters away from the LIDAR sensor tends to diminish.
- Consistency in operation under different lighting and weather conditions
LIDAR systems work at the same different times of the day and in varied weather conditions. The consistency in laser light transmission from LIDAR sensors is independent of environmental conditions. Unlike cameras, this is a suitable choice when data collection is intended to happen at night and in rainy weather.
- Ability to perform 3D mapping
The sophisticated nature of 3D LIDAR sensors allows capturing object information along its vertical plane; thus, the cloud data points are both X, Y, and Z coordinates. This data collected from the surrounding scene is used to construct a 3D map of the target objects, which is crucial in high-resolution 3D imaging.
- Ease of data collection in highly inaccessible areas.
The process of data collection using LIDAR technology is automated. Due to the extensive range of over 100 meters from which object data can be collected using the LIDAR system, 3D mapping of objects located in inaccessible areas, like cliffs, high mountains, is done conveniently without risking lives.
- Automated functionality
Once LIDAR technology is installed and activated, little to no human intervention is needed during data collection because of its automated functionality. That is one reason why it’s suitable for use in areas that are hard to reach. A LIDAR system’s components are designed to work independently of human involvement.
- Safety
With LIDAR technology, you don’t have to climb high mountains or tall trees to measure their heights. Instead, the ease of installation and its capability to collect distant information enables you to gather data from a safe and convenient location.
- Low cost
Suppose you need an accurate data collection system that is fast and dynamic and can save you a lot of money for collecting large volumes of information over a wider area. In that case, LIDAR technology is hard to beat. It’s significantly less costly than other data collection methods.
Cons of LIDAR
- The highly skilled workforce required to operate
LIDAR technology is one of the most complex data collection systems that require high technical and engineering expertise to operate, which is very expensive to acquire. The expert must be rich in surveying knowledge and have a detailed comprehension of how the LIDAR sensor works.
- The high cost of acquisition of LIDAR technology
If you’re considering purchasing a LIDAR system for data collection, you must be prepared to pay a hefty price to acquire a single piece of this technology. As much as most LIDAR systems are costly, some substantially need lower investment, though these may develop technical problems in the long run.
- Too much unnecessary data collected may be costly to process.
The use of LIDAR systems in data gathering results in the collection of massive volumes of data that may otherwise prove challenging and costly to process, especially when the data captured is of unnecessary scenes. For this reason, most data collection companies prefer to subcontract the data processing phase to other equipped companies.
- The invalidity of a single data return
Whereas LIDAR systems are considered the most robust and reliable in collecting and processing large volumes of data, the very process of data gathering might be erroneous, mainly when only a single laser pulse return is used in the calculation of object distance. This error is prevalent in 2D LIDAR systems where inaccurate cloud points can be selected to aid in calculating object distance.
- Lower object recognition capability
Lastly, unlike cameras, LIDAR systems cannot sufficiently scan and identify objects in the surrounding scene to adequately understand the environment to take appropriate action. At best, LIDAR technology can only detect objects and calculate their distance from the LIDAR sensor.
The bottom line
LIDAR technology is considered the most robust software in the data collection and processing industry. This technology uses the time of flight of laser light and the speed of light in air to determine an object’s distance from the light transmitter. As a result, the speed and accuracy achieved in data collected using this approach are astounding. Moreover, large volumes of data can be collected using LIDAR, even in inaccessible areas.
On the flip side, LIDAR technology is costly to acquire and even worse, it requires high-level expertise to operate. Lastly, LIDAR sensors have a lower object recognition capability, among other limitations.