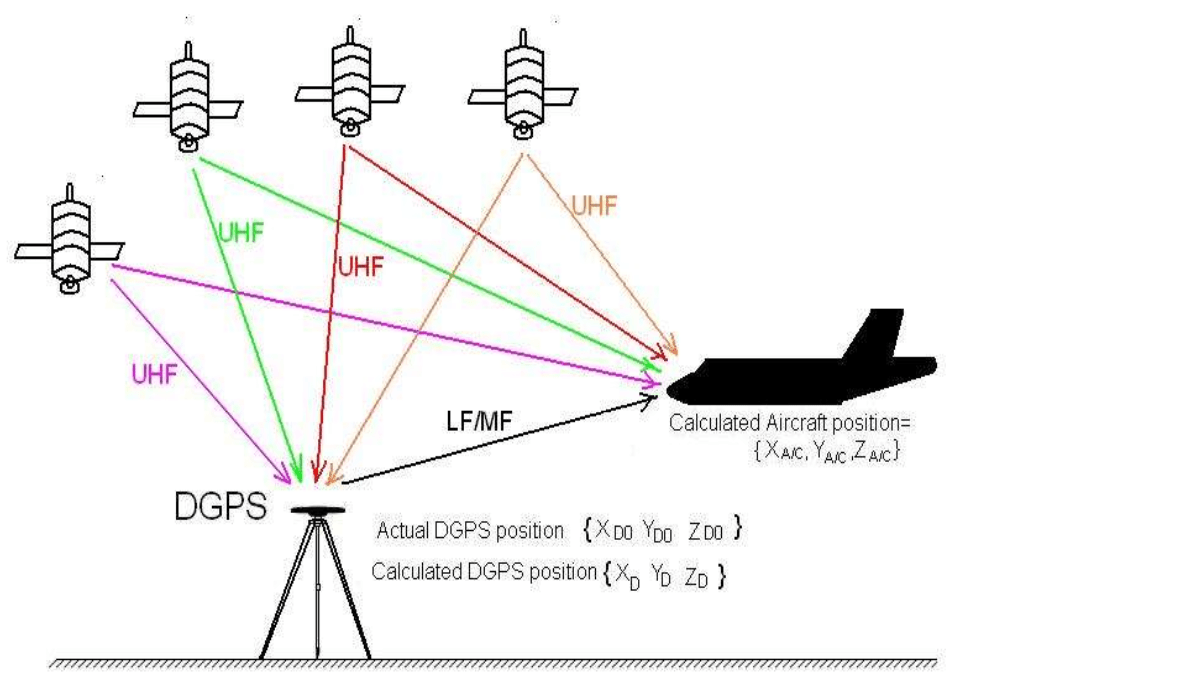
The navigation Systems and location technologies have two systems that are more reliable and globally available. The Global Positioning System ( GPS ) and the Differential GPS ( DGPS ). The GPS is very well known for the robust satellite navigation system it provides for various applications, whereas the DGPS serves as a technique to improve the accuracy of the GPS data with error correction techniques. The DGPS is suitable for applications where very high precision is needed. Where the GPS provides an accuracy of ±15 meters whereas the DGPS has the potential of improving the accuracy drastically to ±3 centimeters.
GPS vs DGPS
| Feature | GPS | DGPS |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | ± 15 meters | ± 3 cm (centimeters) |
| Application Areas | General navigation | High accuracy applications |
| Land Surveying | Limited accuracy | Highly accurate mapping |
| Marine Navigation | Basic navigation | Precise waterway passage |
| Aviation | Standard navigation | Safe takeoff, landing, and in-flight navigation |
| Agriculture | Basic usage | Precision crop management |
| Error Correction | Not applicable | Corrects GPS errors |
| Connection Requirements | None | Requires reference station data |
| Common Techniques | None | Code-based DGPS, Carrier-phase DGPS, SBAS |
| Advantages | Wide coverage, simplicity | High accuracy, reduced errors, enhanced reliability |
| Disadvantages | Limited accuracy | Reference station dependency, potential costs |
| Satellite Signals | L1, L2, L5 frequencies | Same as GPS |
| Water Performance | Doesn’t work underwater | Doesn’t work underwater |
UnderStanding GPS
GPS, which is the Global Positioning System, was originally called the navstar GPS. It is the satellite navigation system developed by the United State government for military purposes. This was used by the military in the early stages for Tactile Ballistic Missiles and by the ground troops for navigation.
The GPS currently consists of 31 satellites that are strategically positioned in the Medium Earth Orbit for global coverage. These satellites emit Electromagnetic signals in a range of frequencies including the L1, L2 and L5 which are received by the receiver and the position is calculated.
Ground Control Stations ( GCS ) And Their Roles
Ground Control Stations ( GCS ) are a group of base stations scattered across the Earth that are used in monitoring the health of the GPS satellites. These base stations performs the Essential task of updating the atomic clocks that are mounted in the satellites and synchronizing them with the ground station clocks for maintaining the accuracy.
Limitations of GPS
- The Satellite Signals can be easily disrupted in the city environments where tall buildings cause a phenomenon called the urban canyon effect.
- The Signals that get reflected by the surfaces and buildings can lead to inaccuracies.
- Adverse weather conditions can cause inaccuracy in GPS calculations
- Potential Signal Jammers can cause GPS outages in the region.
- The Signals from the GPS satellites are mostly weak in penetrating indoors.
- Solar flares and other such events can affect the satellites.
- The GPS is often less accurate in determining the altitude comparing the latitude and longitude
Need For DGPS
Differential GPS ( DGPS ) is a technique that is used to refine and improve the accuracy of the GPS data where higher precision is needed.
The GPS provides an accuracy of ±15 meters whereas the DGPS has the potential of improving the accuracy drastically to ±3 centimeters. This level of improvement is achieved by using highly accurate ground reference points and utilizing error correction techniques.
Real Time DGPS and Post Processing DGPS
There are two types of DGPS, Real Time DGPS and Post Processing DGPS, where the RT-DGPT involves the transmission of error correction data from the base station to the receivers in real time. This method is suitable for Time sensitive applications. Whereas the Post Processing method collects the data from multiple GPS and reference stations, the processing of the data is processed with the GPS data mostly using some type of specialized software for Higher Accuracy.
Applications of DGPS
- Land surveying and mapping. DGPS has revolutionized land surveying and mapping by creating highly accurate maps with detailed distance, angle and elevation data.
- In Marine environments, DGPS provides accuracy needed for navigating the waterways safely by avoiding hazards and maintaining a precise course.
- In the aviation industry, the DGPS is used in ensuring safe takeoffs, landing and in flight navigation.
- The Agriculture industry uses DGPS to map the fields with high accuracy allowing guided machinery to optimize for crop management.
Conclusion
The evolution of navigation technology after the invention of GPS has led to the much improved version of GPS called the DGPS. The GPS provides an accuracy of ±15 meters whereas the DGPS has the potential of improving the accuracy drastically to ±3 centimeters. Therefore to choose between using GPS or DGPS is based on the needs of the application. The application demanding higher precision should go with DGPS and whereas lower precision is deemed enough should go with GPS.