What is GPS and How Does it Work ?
GPS stands for Global Positioning System. It was originally called Navstar GPS. GPS is a satellite based navigation system owned by the United States of America. GPS is one the Global Navigation Satellite System that gives location information, i.e, where the GPS receiver is pointed on the Earth.
The GPS satellites are positioned in the Medium Earth Orbit ( MEO ) to achieve global coverage. There were a total of 83 GPS satellites built and 31 satellites will be operational in orbit at any given point of time. The GPS system requires a minimum of 24 healthy Satellites to provide reliable position data.
How do GPS receivers find the location ?
GPS receivers find the location by sending and receiving the signals from multiple GPS satellites and use a method called trilateration to find the positions from each satellite and pin point accurate location.
GPS Satellite Constellation
The GPS satellites follow constellations that are positioned in a way that ensures that there are at least four satellites visible from any point on the earth. The GPS satellites are MEO ( Medium Earth Orbit ) satellites and are placed at around 20,180 km (12,540 mi) from the Earth.
By Paulsava – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=47209685
How GPS Satellites Transmit Signals?
The GPS satellites transmit signals in 3 different frequencies, L1 (1575.42 MHz), L2 (1227.60 MHz) and more moder GPS uses L5 (1176.45 MHz) frequency for better accuracy and reliability.
Need for Ground Control Stations in GPS Satellites
The Ground Control Stations ( GCS ) are a network of stations in the Earth that monitors the GPS satellites. The role of these stations are to monitor the health of the satellites, update necessary adjustments and to sync up the atomic clock in the satellites with the ground stations to ensure accuracy and reliability in the data provided by the satellites.
Role of Atomic Clock in GPS Satellites
The Atomic clocks are the most reliable clocks known to the man kind and the use of it in GPS satellites is that the current position of the satellites at a given time needs to very precis for the GPS receiver to calculate position with high accuracy. Even a few milliseconds off in the satellite clock can show the GPS position off by a few hundred meters.
How Position is Calculated in GPS
GPS receivers use a method called trilateration to calculate position using GPS. The GPS receivers in the Earth picks up signal from all the available satellites and calculates the distance between them and the satellite using the time taken by the signal to travel from satellites. Then with multiple satellite’s distance data, the position is calculated by triangulating with the known position data from the satellite. This process is known as trilateration and using this, the GPS system to calculate latitude, longitude, altitude, and speed.

By NavigationGuy – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=75898777
Challenges and Limitations
- Signal disruptions in urban areas and dense environments.
- Multipath interference from reflected signals.
- Urban canyon effect with tall buildings obstructing signals.
- Atmospheric interference affects accuracy in adverse weather.
- Potential signal jamming impacting GPS operations.
- Less accurate altitude determination compared to latitude and longitude.
- Space weather events affecting satellite operations.
- Limited indoor performance and accuracy.
- Power consumption affects device battery life.
- Satellite availability influences positioning accuracy.
- Time to fix for initial location determination.
- Privacy concerns with continuous GPS tracking.
Why does GPS not work under water?
The reason why GPS does not work under water is that the electromagnetic waves tend to be absorbed and weakened beyond the useful strength in the water medium. Whereas in contrast sound waves tend to travel effectively in water and die off quickly in air. So, no radar or satellite or any communication that uses Electromagnetic Waves becomes useless under water.
Future of GPS Satellites
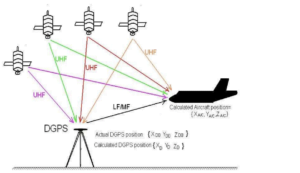
The GPS system has been reliable and accurate for many years. With advancement in technology, the need for more accurate position data is increasing more and more. There are ways to increase accuracy drastically with the help of a method called Differential GPS ( DGPS ). The future of GPS can be such as the integration of current GPS with other nations GNSS systems such as Galileo (European Union) and GLONASS (Russia).
Conclusion
In Conclusion, GPS technology since it was given to the public by the US government, has improved human life drastically and helped other technological advancement in Robotics, self driving cars, food delivery and also simplifies human life for the better.

Pingback: 19 Applications of GPS ( Global Positioning System ) - LIDAR and RADAR
Pingback: GPS vs GLONASS vs Galileo - LIDAR and RADAR
Pingback: 11 Frequently Asked Questions on GPS - LIDAR and RADAR